fungi life cycle explained
Spore Haploid The spore phase is the initial stage of the fungal life cycle. When fungi associate with plants and animals the fungi can donate water minerals or nutrients in exchange for the energy the calories they need to grow.
Fungi can reproduce asexually by budding and many also have sexual reproduction and form fruitbodies.
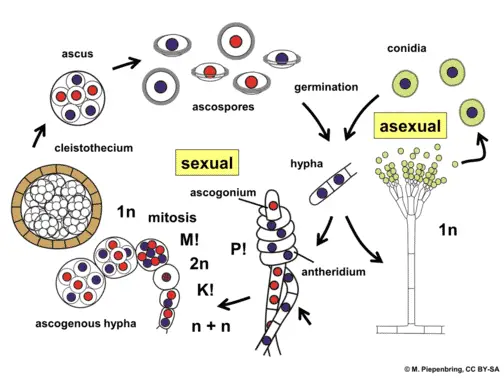
. All fungi begin their life cycle in this stage. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells. 3 Nuclear fusion Karyogamy.
Fungi are eukaryotic non-vascular non-motile and heterotrophic organisms. Bryophytes and Pteridophytes show an intermediate condition called the haplo-diplontic life cycle where phases are multicellular. But that isnt all they do.
Fungi exist primarily as filamentous dikaryotic organisms. Most fungi are microscopic but many produce the visible fruitbodies we call mushrooms. These are called sporangiophores.
The fusion of hyphae is called plasmogamy. The stage during which a fungus reproduces asexually is known as asexual stage or asexual cycle or conidial stage or imperfect stage. Fungi reproduce sexually either through cross- or self-fertilization.
Some fungi do plasmogamy but delay karyogamy forming cells that each have two separate haploid nuclei. Ascomycota are fungi that contain a sac that holds spores during the sexual stage of the life cycle. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion while the diploid phase starts with the formation of the zygote.
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and include yeasts moulds and mushrooms. They may be unicellular or filamentous. There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi.
Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation. Meiosis reduction division restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates the. Organisms that have a haploid life cycle include most fungi with dikaryotic phase algae without dikaryotic phase and male ants and bees.
We can understand the meaning of the term dimorphic just by breaking it into two in which Di means two and Morphic means morphology or structure. Their tips swell to produce a sporangium. Since the sac is one of the most prominent features used to identify members of Ascomycota you.
Fungi Life Cycle Fungi start life as tiny spores. Fungal life cycles are unique and complex. Life cycle of fungi.
When the mycelium grows and develops it might encounter another fungi. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. When a spore lands on favorable real estate depending upon the species this might be a slice of bread a fallen log or a pile of leaves it sends out a thin hair-like tube called a hypha plural hyphae.
Dimorphic fungi can define as a type of fungi which has a dual life cycle. Under favourable climatic conditions the asexual stage may be repeated resulting in the production of conidia in profuse quantities. In this electron micrograph of a mushroom gill the four spores produced by meiosis seen in the center of this picture are carried on a clublike sporangium visible to the left and right.
Haploid fungi form hyphae that have gametes at the tips. Two different mating types represented as type and type are involved. The ascospores produce conidia by budding.
Therefore dimorphic fungi possess two kinds of. In reality there are many sub-steps of the process. The mycelium in most species of Taphrina is annual but in some species it is perennial.
Fungi lack chlorophyll and hence cannot perform photosynthesis. Fungi store their food in the form of starch. After the fungi has become.
Speaking of the lifecycle of fungi in sexually reproducing organisms the haploid and diploid phases alternate. Fungi reproduce sexually either through cross- or self-fertilization. As part of their life cycle fungi produce spores.
The fused hyphae containing haploid nuclei from two individuals is heterokaryotic. In general the life cycle involves the fusion of hyphae from two individuals forming a mycelium that contains haploid nuclei of both individuals. The hypha secretes enzymes that break down the chosen food source.
Two different mating types represented as type and type are involved. They reproduce by means of spores. Some fungi are multicellular while others such as yeasts are unicellular.
The zygote is actually a diploid cell created by the fusion of the two haploid sex cells. The Life Cycle of Fungi. 1 and 2 Dikaryon formation.
The conidia are developed from the ascospores. Asexual reproduction takes place by uninucleate thin-walled spores which are referred to as conidia. These hyphae are called dikaryotic example of fungal life cycle with dikaryotic hyphae.
But this model provides a good overview in terms of how fungi grows from birth to death. Fungal life cycles spores and more. They do take nutrients that are no longer being used and move them to places where they are needed.
4 and 5 Meiosis. A Life cycle of S cerevisiae. All fungi start as haploid spores.
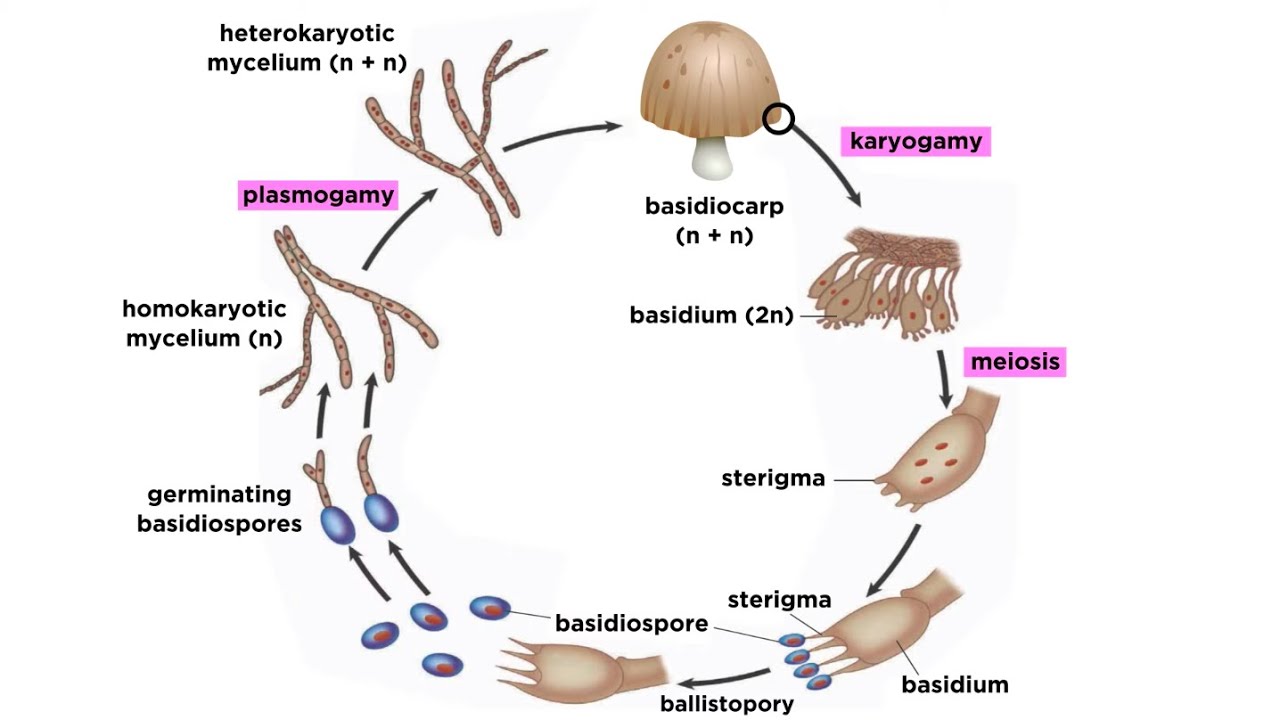
This is the first stage in the life cycle of a fungus. Mycelium Diploid At the point when the mycelium develops and creates it may encounter other fungi. Mushroom dikaryotic mycelium is major phase only when mushroom is formed does karyogamy occur followed by meiosis.
Life Cycle of Fungi. Fungal life cycles are unique and complex. B Basidiospore formation by Filobasidiella neoformans sexual state of Cryptococcus neoformans.
The life cycle of a mushroom begins and ends through five stages of evolutionary phases beginning as a fungal spore seeds and completing its cycle as a mature fruiting body the part of a mushroom we all identify and know that releases new spores to create a new cycle all over again. Haploid fungi form hyphae that have gametes at the tips. If the two fungi are.
Does bryophytes show diplontic life cycle.

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids

Characteristics Of Fungi Boundless Biology

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Fungi Explained Here Is What You Need To Know Microscope Clarity
Life Cycles Of Fungi Biolympiads

Intro To The Fungi Life Cycle Plantsnap

Basidiomycota Life Cycle Study Com

Classifications Of Fungi Openstax Biology 2e
Basidiomycota Part 2 The Mushroom Life Cycle Youtube

Biology Pictures Fungi Life Cycles Fungi Biology

Characteristics Of Fungi Openstax Biology 2e

Draw Life Cycle Diagrams For Plants Fungi And Animals Study Com

Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology For Majors Ii





